Exopolysaccharides
here are the few more exapmples of microbial exoplysaccharides

Curdlan
Curdlan (beta-1,3-glucan) is a high molecular weight polymer composed of glucose. It consists of β-(1,3)-linked glucose residues and forms elastic gels upon heating in aqueous suspension.
It is produced by a non pathogenic bacteria Agrobacterium biobar and Alcaligenes faecalis is being developed to be used in gel production as well
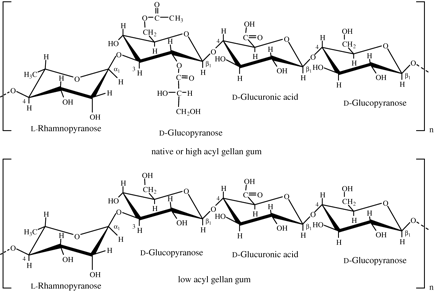
Gellan
It consists of a tetra saccharide, made up of two residues of D-glucose and one of each residues of L-rhamnose and D-glucuronic acid. The tetrasacharide repeat has the following structure:
[D-Glc(β1→4)D-GlcA(β1→4)D-lc(β1→4)L-ha(α1→3)]n.
As it is evident from the figure, the tetrasacharide units are connected by (α1→3) glycosidic bonds.
It is used primarily as a gelling agent, alternative to agar, in microbiological culture. It is able to withstand 120 °C heat, making it especially useful in culturing thermophilic organisms. One needs only approximately half the amount of gellan gum as agar to reach an equivalent gel strength.
Gellan gum is used as gelling agent in plant cell culture on Petri dishes, as it provides a very clear gel, facilitating light microscopical analyses of the cells and tissues.
As a food additive, gellan gum is used as a thickener, emulsifier, and stabilizer.